HTTP Scaler
HTTP Scaler ensures that your service scales based on incoming HTTP requests.
Details
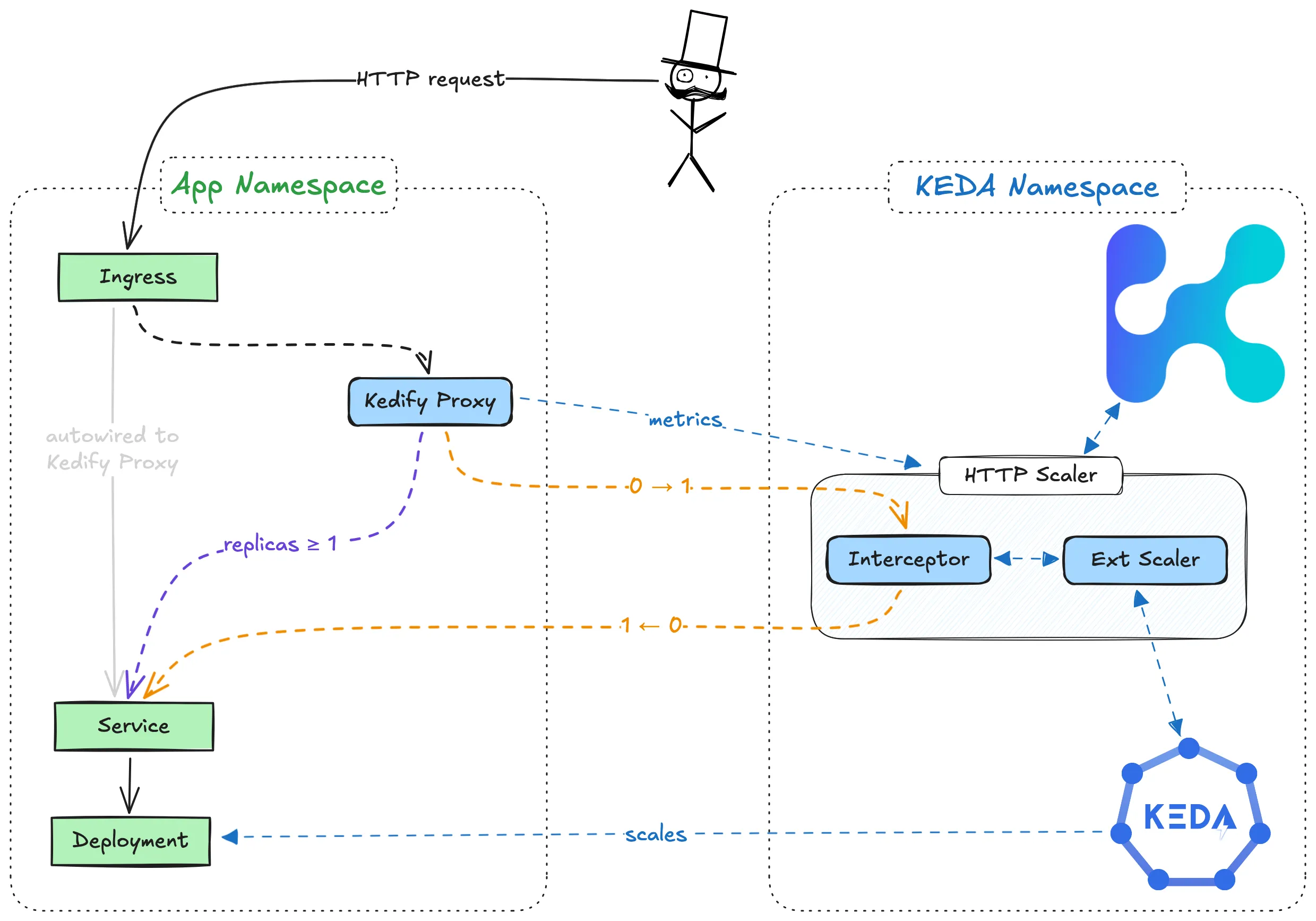
The HTTP scaler is designed specifically for ScaledObject resources to enable scaling based on incoming HTTP traffic; ScaledJob resource is not supported at the moment. It supports automatic scaling, including scaling to zero, without requiring Prometheus or other external components. The scaler monitors traffic using an interceptor proxy and routes traffic accordingly, caching incoming requests when necessary. Additionally, the scaler automatically configures ingress objects for the specified workload.
The scaler supports multiple ingress implementations including Gateway API, Amazon ALB, Istio, and OpenShift Routes, allowing flexibility in managing and monitoring traffic.
Using this scaler, users can define specific hosts and path prefixes to be monitored for traffic. The scaler uses metrics such as request rate or concurrency to determine the scaling needs of the application, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization.
With automatic configuration of ingress objects, the HTTP scaler simplifies the setup process, allowing for seamless integration with existing infrastructure and workloads. This makes it an ideal choice for applications that need to scale based on real-time HTTP traffic.
Architecture
Trigger Specification
This specification describes the kedify-http trigger, which scales workloads based on incoming HTTP traffic.
Here is an example of trigger configuration using the HTTP scaler:
triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: hosts: www.my-app.com service: http-demo-service port: '8080' scalingMetric: requestRate targetValue: '10'Complete parameter list:
Following is a complete list of metadata parameters available for the kedify-http trigger. For better readability, the parameters are grouped into sections:
Routing configuration:
hosts: Comma-separated list of hosts to monitor (e.g.,www.my-app.com,www.foo.bar). This is used for routing the traffic to correct application and uses theHostheader for plaintext HTTP, SNI for TLS, and:authoritypseudo-header for HTTP/2. (Required)pathPrefixes: Comma-separated list of path prefixes to monitor, (e.g.,/foo,/bar, Optional, Default:/).headers: Structured list of HTTP headers to match for routing traffic. See more in dedicated section. (Optional)
Backend serving:
service: Name of the Kubernetes service for the workload specified inScaledObject.spec.scaleTargetRef, where traffic should be routed.fallbackService: Name of the Kubernetes service used as a fallback along withserviceautowiring.port: Port on which the Kubernetes Service is listening. Only one ofportorportNamecan be set.portName: Reference to theportby its name. Only one ofportorportNamecan be set.tlsSecretName: Reference to aSecretcontaining the TLS certificate and key undercert.tls,key.tlsfor TLS passthrough or re-encrypt. Not necessary if using TLS termination at ingress and cluster internal traffic is plaintext (Optional).loadbalancing: Load balancing strategy used when proxying, supportsdns(default behavior, same as empty “ or not defining any), oreds(envoy endpoint discovery service). See also dedicated section for more details. (Optional)
Scaling metrics:
scalingMetric: Metric used for scaling, eitherrequestRateorconcurrency.targetValue: Target value for the scaling metric; KEDA scales out when traffic meets or exceeds this value. (Default:100)granularity: Granularity at which the request rate is measured (e.g., “1s” for one second). (Only forrequestRate, Default:1s)window: Window over which the request rate is averaged (e.g., “1m0s” for one minute). (Only forrequestRate, Default:1m)externalProxyMetricKey: Metric name used for aggregating external source metrics (e.g.,cluster_namefor Envoy, Optional).
Traffic autowiring and healthcheck configuration:
trafficAutowire: Configures traffic autowiring of ingress resources. Settingfalsedisables autowiring; to enable only specific ingress classes, use a comma-separated list (e.g.,httproute,ingress,virtualservice,routeorservice). (See Traffic Autowiring for more details, Optional)healthcheckPath: Healthcheck path on the scaled application for responses when scaled to zero. (See Scaled Application Healthcheck Configuration for more details, Optional)healthcheckPathPrefix: Healthcheck path prefix is only required ifpathEmbeddedHostvalue is set underhealthcheckResponsefield. This path prefix will be stripped from the proxied request as it’s only used for routing to the application (Optional)healthcheckResponse: Response mode for healthchecks, allowed values arepassthrough,static, orpathEmbeddedHost. Only setpassthroughorstaticifhealthcheckPathis specified. ForpathEmbeddedHost, ensure thathealthcheckPathPrefixis also set. (Default:passthrough, Optional)
Static pages configuration:
maintenancePageEnabled: Toggle to enable/disable the maintenance page. Expects a boolean value (trueorfalse). (Default:false, Optional)maintenancePageBody: Inlined HTML body for the maintenance page to override defaults and global configs. This can be configured globally on the http-add-on level or throughConfigMapor omitted which will use the default maintenance page. Limit 256 KiB. (Optional)maintenancePageStatusCode: Inlined HTTP status code for the maintenance page. This too can be configured globally like the body. (Default:503, Optional)maintenancePageConfigMapRef: Reference to aConfigMapcontaining the maintenance page body. TheConfigMapmust be in the same namespace as theScaledObject. (Optional)coldStartWaitingPageEnabled: Toggle to enable/disable the cold-start waiting page. Expects a boolean value (trueorfalse). (Default:false, Optional)coldStartWaitingPageBody: Inlined HTML body for the cold-start waiting page to override defaults and global configs. This can be configured globally on the http-add-on level or throughConfigMapor omitted which will use the default waiting page. Limit 256 KiB. (Optional)coldStartWaitingPageStatusCode: Inlined HTTP status code for the cold-start waiting page. This too can be configured globally like the body. (Default:503, Optional)coldStartWaitingPageConfigMapRef: Reference to aConfigMapcontaining the cold-start waiting page body. TheConfigMapmust be in the same namespace as theScaledObject. (Optional)coldStartWaitingPageRetryAfter: TheRetry-Afterheader value to be returned in the cold-start waiting page response. This can be configured globally on the http-add-on level or throughConfigMapor omitted which will use the default. (Default:10s, Optional)
Example ScaledObject with HTTP trigger
Here is a full example of a scaled object definition using the HTTP trigger:
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1kind: ScaledObjectmetadata: name: http-demo-scaledobjectspec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: http-demo-deployment cooldownPeriod: 5 minReplicaCount: 0 maxReplicaCount: 10 triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: hosts: www.my-app.com pathPrefixes: '/' service: http-demo-service port: '8080' scalingMetric: requestRate targetValue: '10' granularity: '1s' window: '1m0s'Note: Ensure that
hosts,pathPrefixes,service, andportparameters match the application’s routing requirements.
Traffic Autowiring:
Kedify automatically re-wires ingress resources for the following implementations:
In a typical Kubernetes setup, the networking configuration is structured as follows:
Ingress -> Service -> Deployment
To enable automatic scaling based on incoming HTTP traffic, Kedify introduces additional components:
- kedify-proxy: An Envoy-based proxy that routes traffic and collects metrics for scaling.
- HTTP Add-on Interceptor: Ensures requests are routed and cached when the app is scaled to zero.
With Kedify, the traffic flow includes these additional components:
Ingress -> kedify-proxy -> Service -> Deployment
For finer control over ingress resources autowiring, use trafficAutowire with a comma-separated list of resources to be autowired, including route for OpenShift Routes.
triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: trafficAutowire: 'httproute,ingress,virtualservice,route'Autowiring Fallback
In case of control plane issues with kedify-proxy or interceptor, Kedify rewires traffic back to the original flow:
Ingress -> Service -> Deployment
This fallback avoids outages and keeps the application accessible. By default, traffic is rewired if Kedify detects control plane issues for over 5 seconds. This duration can be configured using HTTP_HEALTHCHECK_DEBOUNCER_SECONDS on the Kedify Agent deployment.
Disabling Traffic Autowiring
To disable traffic autowiring, specify:
triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: trafficAutowire: 'false'In this case, users must manually wire the networking traffic. Note that Autowiring Fallback does not apply here.
Service Autowiring
For applications that are used only within the cluster and exposed only as a Service but would like to benefit from HTTP traffic autoscaling along with fallback, there is also service level autowiring. Configuring service as the trafficAutowire option excludes setting any other trafficAutowire options because it effectively replaces all of them. Kedify Agent will wire the traffic by managing Kubernetes Endpoints belonging to the Services defined in service and fallbackService in the trigger metadata.
This type of traffic autowiring brings two more requirements on the application and autoscaling manifests:
- ScaledObject must define
fallbackService: because the Kedify Agent uses it for injecting Endpoints to theservicedefined in the trigger metadata andkedify-proxyfor routing. - Application service must NOT have selector defined: the Kubernetes control plane manages Endpoints for Services with selectors, which would collide with autowire feature. The
servicedefined in the trigger metadata must be without selector while thefallbackServiceshould carry the original selector you’d define on theserviceif it wasn’t autowired.
There is a redundancy periodic sync for service autowiring to ensure the Endpoints are always up to date. The sync interval defaults to 500ms and is configurable using the KEDIFY_AUTOWIRE_SERVICE_SYNC_PERIOD environment variable on the Kedify Agent and can be further fine tuned by poviding http.kedify.io/service-resync-period annotation on the ScaledObject resource.
Kedify Proxy
The Kedify HTTP Scaler uses the kedify-proxy (Envoy) to route traffic and collect metrics for applications, enhancing reliability and performance. This proxy setup helps prevent potential bottlenecks in the interceptor. Currently, Envoy is the only natively supported proxy for the HTTP Scaler; other reverse proxy solutions may require additional configuration.
Deployment Options for Kedify Proxy
There are two main deployment configurations for kedify-proxy: Namespace-Level and Cluster-Wide.
-
Namespace-Level Deployment (Default): By default,
kedify-proxyis deployed in each namespace that contains at least oneScaledObjectusing thekedify-httptrigger. This approach ensures that traffic routing and metric collection are confined within the namespace where theScaledObjectis defined, providing isolation and control. -
Cluster-Wide Deployment (Optional): For environments where Istio’s VirtualService is used (currently the only supported configuration),
kedify-proxycan be deployed cluster-wide. In this setup,kedify-proxyis deployed in the KEDA installation namespace and shared among allScaledObjectsacross namespaces. This configuration allows centralized traffic routing and scaling across all namespaces in the cluster.- To enable cluster-wide deployment, set the environment variable
KEDIFY_PROXY_CLUSTER_WIDEtotrueon the Kedify Agent. This will configure the Kedify Agent to deploy a single instance ofkedify-proxyfor the entire cluster, located in the KEDA installation namespace. For more details, refer to the Kedify Agent documentation.
- To enable cluster-wide deployment, set the environment variable
Note: The cluster-wide setup for
kedify-proxyis only compatible with Istio’s VirtualService. Other types of ingress configurations are not supported in this setup.
Configuring Kedify Proxy Replica Count
The kedify-proxy deployment has a default replica count of 1, which can be adjusted to meet specific performance or redundancy requirements within a namespace or across the cluster.
To configure a different default replica count globally, set the environment variable KEDIFY_PROXY_DEFAULT_REPLICA_COUNT to a valid integer N on the Kedify Agent:
env: - name: KEDIFY_PROXY_DEFAULT_REPLICA_COUNT value: 'N'This setting applies to each kedify-proxy deployment, adjusting the number of proxy replicas for improved scalability or availability as needed.
Kedify Proxy Traffic Flow
When using Kedify, the traffic flow in Kubernetes is enhanced to include additional components for real-time monitoring and scaling based on HTTP traffic. Typically, Kubernetes follows this traffic pattern:
Ingress -> Service -> Deployment
With Kedify, the traffic flow includes kedify-proxy as an intermediary to monitor and intercept traffic before it reaches the service:
Ingress -> kedify-proxy -> Service -> Deployment
The kedify-proxy intercepts, routes, and caches HTTP requests when necessary. This routing allows the scaler to collect traffic metrics and adjust replica counts based on real-time demands. For more details on autowiring and traffic routing configurations, refer to the Traffic Autowiring section.
Kedify Proxy Environment Variables Summary
Here’s a summary of the key environment variables used for configuring kedify-proxy. These are expected to be configured on kedify-agent deployment:
-
KEDIFY_PROXY_CLUSTER_WIDE: Enables the cluster-wide deployment ofkedify-proxyin the KEDA installation namespace, shared across all namespaces in the cluster. This variable should be set totrueon the Kedify Agent for a cluster-wide configuration. This setup is only compatible with Istio’s VirtualService. For more information, see the Kedify Agent documentation. -
KEDIFY_PROXY_DEFAULT_REPLICA_COUNT: Sets the default number of replicas for eachkedify-proxydeployment. This variable should be set to a valid integerNon the Kedify Agent to adjust the global replica count as per performance or availability requirements. -
KEDIFY_PROXY_LOG_FORMAT: Environment variable defined on the Kedify Agent specifies the log format for thekedify-proxyfleet. Supports two options,plaintextandjson, with default beingplaintext. orkeda-add-ons-http-interceptor
And these are expected to be configured on keda-add-ons-http-interceptor deployment:
-
KEDIFY_PROXY_ACCESS_LOG_TYPE: Enable access logs forkedify-proxyfleet. Supports three options,plaintext,json, and “ to disable access logs. By default, access logs are disabled. -
KEDA_HTTP_CUSTOM_{INTERCEPTOR,KEDIFY_PROXY}_{REQUEST,RESPONSE}_HEADERS: Comma-separated list of custom headers with values added to the proxied request or response by interceptor or kedify-proxy. By default, no custom headers are added. Example:KEDA_HTTP_CUSTOM_INTERCEPTOR_REQUEST_HEADERS=header1:value1,header2:value2.
Multiple HTTP Triggers Per ScaledObject
Starting with Kedify version 2.17.1-1, the HTTP scaler now supports defining multiple kedify-http triggers within a single ScaledObject. This enhancement allows a single autoscaled workload to respond to multiple independent HTTP traffic patterns, each defined by its own trigger.
When configuring multiple HTTP triggers in a single ScaledObject, the following constraints must be observed:
-
Unique
trigger.namerequired: Eachkedify-httptrigger must specify a uniquetrigger.nameto differentiate metrics and routing behavior. -
Distinct routing configurations: Each trigger must define either:
- Different
hosts, or - If the
hostsare the same, differentpathPrefixes, or - If both
hostsandpathPrefixesare the same, then differentheaders.
- Different
This ensures unambiguous routing and avoids conflicts in traffic interception logic.
Example: Multiple HTTP Triggers
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1kind: ScaledObjectmetadata: name: multi-trigger-demospec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: http-demo-deployment cooldownPeriod: 5 minReplicaCount: 0 maxReplicaCount: 10 triggers: - type: kedify-http name: primary metadata: hosts: www.my-app.com pathPrefixes: '/primary' service: http-demo-service port: '8080' scalingMetric: requestRate targetValue: '10' - type: kedify-http name: secondary metadata: hosts: www.my-app.com pathPrefixes: '/secondary' service: http-demo-service port: '8080' scalingMetric: requestRate targetValue: '5'This configuration routes and scales independently for /primary and /secondary traffic paths on the same host, reusing the same application service but with isolated triggers.
Refer to the Trigger Specification section for full details on configuring each kedify-http trigger.
Scaled Application Healthcheck Configuration
Configuring healthchecks for applications typically excludes unhealthy replicas from load balancing. However, this conflicts with scaling to zero, as healthchecks generate HTTP traffic, triggering scale-up actions.
Kedify’s interceptor can respond to healthchecks on behalf of the scaled application instead of proxying the check to the application and causing a scale-out. Healthcheck path and response mode (default passthrough, or static) can be defined for the scaled application. Passthrough mode allows the interceptor to respond only if the application is scaled to zero; otherwise, it proxies the request.
triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: healthcheckPath: '/healthz' healthcheckResponse: 'passthrough' # or 'static'Preconfigured healthcheck paths are excluded from metric counting.
Example ScaledObject with Healthcheck Configuration
The following configuration instructs the interceptor to respond to requests for www.my-app.com/healthz when scaled to 0:
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1kind: ScaledObjectmetadata: name: http-demo-scaledobjectspec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: http-demo-deployment cooldownPeriod: 5 minReplicaCount: 0 maxReplicaCount: 10 triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: hosts: www.my-app.com pathPrefixes: '/' service: http-demo-service port: '8080' scalingMetric: requestRate targetValue: '10' healthcheckPath: '/healthz' healthcheckResponse: 'passthrough'Healthchecks for AWS Probes
Because AWS Load Balancer healthcheck probes set the IP address of a particular kedify-proxy pod as a value for the Host header, there is additional requirement to uniquely identify the proxied application through their healthcheck paths. This can be done by setting the healthcheckResponse: pathEmbeddedHost and healthcheckPathPrefix parameter in the trigger metadata.
The interceptor will strip this prefix from the proxied request before sending it to the application as the prefix is only used for routing purposes. This means each healthcheckPathPrefix should be unique across all ScaledObjects in the cluster.
Example:
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1kind: ScaledObjectmetadata: name: http-demo-scaledobjectspec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: http-demo-deployment cooldownPeriod: 5 minReplicaCount: 0 maxReplicaCount: 10 triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: hosts: www.my-app.com pathPrefixes: '/' service: http-demo-service port: '8080' scalingMetric: requestRate targetValue: '10' healthcheckPathPrefix: '/kedify-proxy/www.my-app.com' healthcheckResponse: 'pathEmbeddedHost'Then in the AWS loadbalancing target groups, the healthcheck path can be set as for example /kedify-proxy/www.my-app.com/health, and the application will receive the request on the /health endpoint. Because each probe is forwarded to the application, it is not well-suited for scale-to-zero scenarios. It can still be used, but each probe request will result in a scale out action.
Maintenance Page and Cold-Start Waiting Page Configuration
-
Maintenance page: For planned downtime or scheduled maintenance, Kedify provides the option to display a custom static page (up to 256 KiB) that notifies users of the service interruption and offers an estimated return time.
-
Cold-Start Waiting page: When the application needs extra time to scale out, Kedify can immediately serve a custom waiting page (up to 256 KiB) that delivers clear information to users while the service is booting up.
The HTTP scaler supports serving a static maintenance page / cold-start waiting page directly from the interceptor. When enabled, incoming requests receive a preconfigured response. For maintenance page, scaling metrics are disregarded although the interceptor endpoint /queue continues displaying actual request metrics, but these metrics are ignored by the scaler (replaces the value with 0 and sets active status to false), effectively disabling scaling actions during maintenance mode.
Maintenance Page Parameters:
maintenancePageEnabled: Toggle to enable or disable the maintenance page. Accepts boolean values (trueorfalse). (Default:false, Optional)maintenancePageBody: Inline HTML content for a custom maintenance page. Overrides defaults or global configurations. Maximum size is 256 KiB. (Optional)maintenancePageStatusCode: Custom HTTP status code returned during maintenance mode. Overrides default or global configuration. (Default:503, Optional)maintenancePageConfigMapRef: Reference to aConfigMapin the same namespace as theScaledObjectcontainingmaintenancePageBodyandmaintenancePageStatusCode. (Optional)
Cold-Start Waiting Page Parameters:
coldStartWaitingPageEnabled: Toggle to enable or disable the cold-start waiting page. Accepts boolean values (trueorfalse). (Default:false, Optional)coldStartWaitingPageBody: Inline HTML content for a custom cold-start waiting page. Overrides defaults or global configurations. Maximum size is 256 KiB. (Optional)coldStartWaitingPageStatusCode: Custom HTTP status code returned during cold-start waiting mode. Overrides default or global configuration. (Default:503, Optional)coldStartWaitingPageConfigMapRef: Reference to aConfigMapin the same namespace as theScaledObjectcontainingcoldStartWaitingPageBody,coldStartWaitingPageStatusCode, andcoldStartWaitingPageRetryAfter. (Optional)coldStartWaitingPageRetryAfter: TheRetry-Afterheader value to be returned in the cold-start waiting page response. This can be configured globally on the http-add-on level or throughConfigMapor omitted which will use the default. (Default:10s, Optional)
For more details, see Configure Waiting and Maintenance Pages for HTTP Scaler how-to page.
Routing Traffic with HTTP Headers
On top of the default routing based on hosts and pathPrefixes, Kedify allows routing traffic based on HTTP headers. This feature is useful for applications that require specific routing logic where multiple autoscaled services serve the same host and path but differ in HTTP headers, for example for A/B testing or canary deployments.
To configure this, you can use the headers parameter in the trigger metadata:
triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: hosts: www.my-app.com pathPrefixes: '/' service: http-demo-service headers: | - name: X-My-Header value: header-valueFor hosts and pathPrefixes routing, the algorithm doesn’t support multiple ScaledObjects with the same hosts and pathPrefixes parameters. This is because the routing algorithm uses the longest path prefix substring to match the pathPrefixes parameter, and if there are multiple ScaledObjects with the same hosts and pathPrefixes, it would be impossible to determine which one to route to.
However, with the header-based routing it’s possible to configure multiple ScaledObjects with triggers that match the same hosts and pathPrefixes but differ in the headers parameter. This allows for more granular control over routing and scaling based on specific HTTP headers.
- The
Hostheader for plaintext HTTP, SNI for TLS and:authoritypseudo-header for HTTP/2 is used to match thehostsparameter. - When there are multiple
HTTPScaledObjects, the longest path prefix substring is used to match thepathPrefixesparameter. - If there are still multiple
HTTPScaledObjectsmatching, select the one with the mostheadersmatching.
Load Balancing Strategy
Kedify HTTP Scaler supports two load balancing strategies for routing traffic through the kedify-proxy:
- DNS Load Balancing (default): In the trigger metadata in
loadbalancingfield configuredns(or “ or omit the field entirely). This strategy uses DNS to resolve the service’s endpoints and balances traffic across them. It is the default behavior and does not require any additional configuration. - Envoy Endpoint Discovery Service (EDS): In the trigger metadata in
loadbalancingfield configureeds. This strategy uses Envoy’s EDS to dynamically discover and balance traffic across service endpoints fromEndpointSlicesKubernetes API. This setup results in more frequent envoy configuration updates but can improve routing for applications without readiness probes or graceful terminations.
Snippet of a trigger with eds Load Balancing Strategy:
triggers: - type: kedify-http metadata: loadbalancing: eds ...